Azure DevOps: 7 Powerful Features You Must Know in 2024
If you’re building software in 2024, ignoring Azure DevOps is like coding without version control—risky and outdated. This powerful platform unifies development, operations, and collaboration, making it a must-have for modern teams. Let’s dive into why Azure DevOps is a game-changer.
What Is Azure DevOps and Why It Matters

Azure DevOps is Microsoft’s comprehensive suite of cloud-based services designed to support the entire software development lifecycle. From planning and coding to testing, deployment, and monitoring, it offers a seamless, integrated experience for development teams of all sizes. Whether you’re a solo developer or part of a global enterprise, Azure DevOps provides the tools to streamline workflows, enhance collaboration, and accelerate delivery.
Core Components of Azure DevOps
Azure DevOps isn’t a single tool but a collection of five key services that work together to support DevOps practices:
- Azure Repos: Git repositories or Team Foundation Version Control (TFVC) for source code management.
- Azure Pipelines: CI/CD (Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery) for automating builds and deployments.
- Azure Boards: Agile planning tools like Kanban boards, backlogs, and work item tracking.
- Azure Test Plans: Manual and exploratory testing tools to ensure software quality.
- Azure Artifacts: Package management for sharing libraries and dependencies across teams.
These components can be used together or independently, offering flexibility based on team needs. For example, a startup might only use Azure Repos and Pipelines, while a large enterprise could leverage all five services for end-to-end traceability.
How Azure DevOps Fits into Modern DevOps Culture
DevOps is not just a set of tools—it’s a cultural shift that emphasizes collaboration, automation, and rapid feedback. Azure DevOps supports this culture by breaking down silos between development and operations teams. With real-time dashboards, automated pipelines, and integrated testing, teams can deliver value faster and with higher quality.
According to Microsoft, organizations using Azure DevOps report up to a 50% reduction in deployment failures and a significant increase in deployment frequency. This is because the platform enables consistent environments, automated testing, and rollback capabilities—key pillars of DevOps success.
“Azure DevOps bridges the gap between idea and production, enabling teams to ship software with confidence.” — Microsoft Azure Documentation
Azure DevOps vs. Competitors: A Strategic Comparison
While several platforms offer DevOps capabilities, Azure DevOps stands out due to its deep integration with Microsoft’s ecosystem, enterprise-grade security, and hybrid deployment options. Let’s compare it with some major competitors.
Azure DevOps vs. GitHub Actions
GitHub Actions, now part of Microsoft, shares many features with Azure DevOps, especially in CI/CD. However, Azure DevOps offers a more comprehensive suite. While GitHub Actions excels in open-source collaboration and simplicity, Azure DevOps provides advanced project management (via Boards), test planning, and artifact management—features not natively available in GitHub.
Moreover, Azure DevOps allows you to connect to any Git repository, including GitHub, giving you the flexibility to use your preferred code hosting while still benefiting from Azure’s robust pipelines and boards.
Azure DevOps vs. Jenkins
Jenkins is a popular open-source automation server, but it requires significant setup and maintenance. Azure DevOps, being cloud-native, reduces infrastructure overhead. It offers managed agents, built-in security, and automatic scaling—features that Jenkins users must configure manually.
For teams looking to reduce operational complexity, Azure DevOps is often the better choice. However, Jenkins remains popular for highly customized workflows or on-premises environments where full control is required.
Azure DevOps vs. GitLab CI/CD
GitLab offers a complete DevOps platform similar to Azure DevOps, with integrated source control, CI/CD, monitoring, and security. The key difference lies in ecosystem alignment. GitLab is language-agnostic and open-core, while Azure DevOps integrates seamlessly with .NET, Visual Studio, and Microsoft Azure services.
Enterprises already invested in Microsoft technologies often find Azure DevOps easier to adopt and manage, especially when compliance, identity management (via Azure AD), and hybrid cloud strategies are involved.
Setting Up Your First Azure DevOps Project
Getting started with Azure DevOps is straightforward. Whether you’re building a web app, mobile service, or microservices architecture, the setup process follows a consistent pattern.
Creating an Organization and Project
1. Go to dev.azure.com and sign in with your Microsoft account.
2. Click “Create Organization” and follow the prompts.
3. Once your organization is set up, create a new project. You can choose between Agile, Scrum, or CMMI process templates.
4. Select version control (Git or TFVC) and visibility (public or private).
This project becomes your central hub for code, work items, builds, and releases.
Inviting Team Members and Managing Permissions
Collaboration is at the heart of Azure DevOps. You can invite team members via email and assign roles such as Stakeholder, Contributor, or Project Administrator.
Permissions are granular. For example, you can restrict who can approve pull requests, delete branches, or view sensitive work items. Integration with Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) ensures secure, centralized identity management—especially useful for large enterprises.
Connecting IDEs and Development Tools
Azure DevOps integrates with popular IDEs like Visual Studio, Visual Studio Code, IntelliJ, and Eclipse. Using the Azure DevOps extension for VS Code, developers can clone repositories, create branches, and push code directly from their editor.
You can also use the Azure CLI or REST APIs for automation and scripting, enabling infrastructure-as-code workflows and CI/CD pipeline customization.
Mastering Azure Repos: Version Control Done Right
Azure Repos is the foundation of any Azure DevOps project. It provides enterprise-grade Git repositories with advanced features for code collaboration and security.
Working with Git Repositories in Azure DevOps
When you create a new project, Azure Repos automatically sets up a Git repository. You can clone it using HTTPS or SSH:
git clone https://dev.azure.com/yourorg/yourproject/_git/yourrepo
Branching strategies like Git Flow or GitHub Flow can be implemented easily. Azure Repos supports branch policies, which enforce rules such as mandatory code reviews, status checks, and minimum reviewer counts before merging.
Branch Policies and Pull Request Automation
Branch policies are critical for maintaining code quality. You can configure them under Repos > Branches in the web portal. Key settings include:
- Require a minimum number of reviewers
- Automatically include code reviewers based on file paths
- Require linked work items to track feature progress
- Check for linked pull requests in commits
- Require successful builds before merging
These policies ensure that no code lands in the main branch without proper validation, reducing bugs and improving accountability.
Securing Code with Access Controls and Auditing
Azure Repos allows fine-grained permissions at the repository, branch, and even file level. You can deny read, write, or merge access to specific users or groups.
Additionally, audit logs track every push, pull, and permission change. This is crucial for compliance with standards like ISO 27001, SOC 2, or GDPR. Audit data can be exported and integrated with SIEM tools for centralized monitoring.
Automating Workflows with Azure Pipelines
Azure Pipelines is the engine of automation in Azure DevOps. It supports CI/CD for virtually any language, platform, or cloud—making it one of the most flexible pipeline systems available.
Building CI/CD Pipelines for Any Language
Whether you’re using .NET, Node.js, Python, Java, or Go, Azure Pipelines can build and deploy your application. It uses YAML-based pipeline definitions, which are stored in your repository (infrastructure as code).
Example of a simple Node.js pipeline:
trigger:
- main
pool:
vmImage: 'ubuntu-latest'
steps:
- task: NodeTool@0
inputs:
versionSpec: '16.x'
displayName: 'Install Node.js'
- script: |
npm install
npm run build
npm test
displayName: 'npm install, build, and test'This pipeline runs on every push to the main branch, ensuring fast feedback.
Using Self-Hosted vs. Microsoft-Hosted Agents
Azure Pipelines offers two types of build agents:
- Microsoft-hosted agents: Pre-configured virtual machines (Windows, Linux, macOS) that spin up on demand. Ideal for most scenarios due to ease of use and maintenance.
- Self-hosted agents: Run on your own infrastructure. Useful when you need specific software, access to internal networks, or compliance with data residency laws.
Self-hosted agents require more setup but give you full control over the environment.
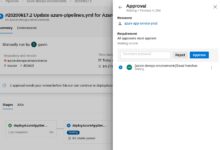
Implementing Multi-Stage Deployments and Approvals
Complex applications often require deployment to multiple environments (dev, staging, production). Azure Pipelines supports multi-stage YAML pipelines with manual approvals, gates, and deployment conditions.
For example, you can configure a pipeline to deploy to staging automatically but require a manual approval before production. You can also integrate with Azure Monitor or Application Insights to validate performance before promoting a release.
Enhancing Collaboration with Azure Boards
Azure Boards is where planning meets execution. It provides agile tools to manage work, track progress, and align teams around shared goals.
Managing Work Items and Backlogs
Work items in Azure Boards can represent user stories, bugs, tasks, or epics. Teams can prioritize them in backlogs and organize sprints. The drag-and-drop interface makes it easy to update status, assign owners, and estimate effort using story points.
Backlogs can be sliced by area, iteration, or team, enabling large organizations to manage multiple projects within a single Azure DevOps organization.
Customizing Workflows and Process Templates
Azure Boards supports three default process templates: Agile, Scrum, and CMMI. Each defines a different workflow for work items. You can also create a custom process to match your team’s methodology.
For example, you might add a “Security Review” state to your bug workflow or create a new work item type for compliance audits. These customizations ensure that Azure Boards adapts to your process—not the other way around.
Visualizing Progress with Dashboards and Queries
Dashboards in Azure Boards provide real-time visibility into team performance. You can add widgets for burndown charts, build status, test results, and more.
Queries allow you to filter and group work items dynamically. For instance, you can create a query to show all high-priority bugs assigned to the current sprint. These queries can be saved, shared, and used in reports or dashboards.
Ensuring Quality with Azure Test Plans and Artifacts
Delivering software fast means nothing if it’s full of bugs. Azure DevOps includes tools to ensure quality at every stage.
Running Manual and Exploratory Testing
Azure Test Plans provides structured test case management. You can define test steps, expected results, and assign tests to team members. Testers can run test suites and log results directly in the browser.
Exploratory testing allows testers to discover issues without predefined scripts. Sessions are recorded, including screenshots and logs, making it easier to reproduce and fix bugs.
Managing Packages with Azure Artifacts
Azure Artifacts enables teams to create and share NuGet, npm, Maven, and Python packages. You can set up private feeds to control access to internal libraries.
For example, your frontend team can publish a shared UI component library, and the backend team can consume it without exposing it publicly. Integration with Azure Pipelines ensures packages are versioned and deployed automatically.
Integrating Testing into CI/CD Pipelines
Automated tests should run on every build. Azure Pipelines can execute unit, integration, and UI tests using frameworks like Jest, JUnit, Selenium, or Playwright.
Test results are published and visible in the pipeline summary. Failed tests block deployments, ensuring only high-quality code reaches production. You can also upload code coverage reports to track testing completeness.
Scaling Azure DevOps for Enterprise Teams
As organizations grow, so do their DevOps needs. Azure DevOps scales from small teams to global enterprises with thousands of users.
Managing Multiple Projects and Organizations
You can create multiple projects within a single Azure DevOps organization. Each project can have its own repositories, pipelines, and teams. This is useful for isolating products or departments while maintaining centralized billing and administration.
For even larger scale, you can create multiple organizations—ideal for separating environments like production, development, or partner collaborations.
Enforcing Security and Compliance Policies
Enterprise-grade security is built into Azure DevOps. Features include:
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
- Private endpoints and service endpoints for network security
- Data encryption at rest and in transit
- Audit logs and export capabilities
- Compliance with ISO, SOC, HIPAA, and GDPR
Administrators can enforce policies like two-factor authentication (2FA) and conditional access using Azure AD.
Integrating with Third-Party Tools and Services
Azure DevOps integrates with hundreds of tools via the Azure DevOps Marketplace. Popular integrations include:
- Jira (bidirectional sync)
- Slack (pipeline notifications)
- SonarQube (code quality analysis)
- Checkmarx (security scanning)
- Datadog (monitoring)
These integrations extend Azure DevOps’ capabilities without requiring custom development.
What is Azure DevOps used for?
Azure DevOps is used to manage the entire software development lifecycle. It supports version control (Azure Repos), continuous integration and delivery (Azure Pipelines), agile project management (Azure Boards), testing (Azure Test Plans), and package management (Azure Artifacts). It’s ideal for teams looking to automate workflows, improve collaboration, and deliver software faster and more reliably.
Is Azure DevOps free to use?
Yes, Azure DevOps offers a free tier for small teams. It includes unlimited private repositories, 30,000 minutes of CI/CD per month, and up to five free users. Additional users and resources can be added via paid plans. There’s also a free tier for open-source projects.
How does Azure DevOps integrate with GitHub?
Azure DevOps can connect to GitHub repositories directly. You can trigger pipelines when code is pushed to GitHub, use GitHub issues with Azure Boards, and even manage GitHub packages in Azure Artifacts. This hybrid approach allows teams to leverage GitHub’s community while using Azure’s advanced CI/CD and project management features.
Can Azure DevOps deploy to non-Azure environments?
Absolutely. Azure Pipelines can deploy applications to any cloud (AWS, Google Cloud), on-premises servers, Kubernetes clusters, or even virtual machines. It uses agents and deployment groups to reach any target environment, making it a truly platform-agnostic DevOps solution.
What are the best practices for using Azure DevOps?
Best practices include using YAML pipelines for version-controlled CI/CD, enforcing branch policies, integrating automated testing, leveraging Azure Boards for agile planning, and using Azure Artifacts for dependency management. Also, regularly audit permissions and use dashboards to monitor team performance and pipeline health.
Microsoft’s Azure DevOps is more than just a tool—it’s a complete ecosystem for modern software delivery. From its robust CI/CD pipelines to its collaborative agile boards, it empowers teams to build, test, and deploy with confidence. Whether you’re a startup or a Fortune 500 company, Azure DevOps provides the scalability, security, and flexibility needed to thrive in today’s fast-paced development landscape. By mastering its features and integrating them into your workflow, you’re not just adopting a platform—you’re embracing a culture of continuous improvement and innovation.
Further Reading: