Azure Portal: 7 Ultimate Features You Must Master Today
Welcome to the ultimate guide on the Azure Portal — your gateway to managing Microsoft’s cloud empire. Whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned admin, mastering this powerful interface is non-negotiable in today’s cloud-driven world.
What Is the Azure Portal and Why It Matters

The Azure Portal is Microsoft’s web-based interface for managing cloud services, resources, and subscriptions within the Azure ecosystem. It serves as the central command center for deploying, monitoring, and securing cloud infrastructure. Unlike command-line tools or APIs, the portal offers a visual, intuitive experience that simplifies complex cloud operations.
Definition and Core Purpose
The Azure Portal, officially known as the Azure Management Portal, is a unified dashboard that allows users to interact with Azure services. From creating virtual machines to configuring AI models, everything can be orchestrated through this single interface. Its primary purpose is to abstract the complexity of cloud computing into manageable, clickable workflows.
Evolution from Classic to Modern Portal
Originally launched as the ‘Azure Classic Portal’ in 2010, the interface was limited in functionality and scalability. In 2015, Microsoft introduced the modern Azure Portal, rebuilt with a responsive design, role-based access control (RBAC), and deeper integration with Azure Resource Manager (ARM). This shift marked a significant leap toward enterprise-grade cloud management.
Key Users and Their Roles
- Cloud Administrators: Manage subscriptions, enforce policies, and monitor usage.
- Developers: Deploy applications, configure CI/CD pipelines, and debug services.
- Security Teams: Audit access logs, set up threat detection, and manage identity policies.
- Finance Managers: Track spending, set budgets, and generate cost reports.
Each role interacts with the Azure Portal differently, but all rely on its centralized visibility and control.
“The Azure Portal isn’t just a dashboard — it’s the cockpit of your cloud infrastructure.” — Microsoft Cloud Architect, 2023
Navigating the Azure Portal Interface Like a Pro
Mastering navigation is the first step to unlocking the full potential of the Azure Portal. The interface is designed for efficiency, but its depth can overwhelm newcomers. Let’s break down its layout and navigation tools.
Dashboard and Home Screen Customization
When you log in, you land on a customizable dashboard. You can pin frequently used resources, create multiple dashboards for different teams, and even share them across users. For example, a DevOps team might have a dashboard showing deployment statuses, while a security team monitors active alerts.
To customize, click ‘Edit Dashboard’, drag and drop tiles, and save views. Microsoft provides pre-built templates, but the real power lies in personalization.
Resource Groups and Subscription Management
Everything in Azure is organized under subscriptions, which are billing and governance boundaries. Within subscriptions, resource groups act as logical containers for related resources (e.g., a web app and its database).
In the Azure Portal, you can filter by subscription, move resources between groups, and apply tags for better organization. This hierarchical structure is crucial for cost tracking and compliance.
Search, Filters, and Quick Find Tools
The global search bar at the top is one of the most underutilized features. Type any service name (e.g., ‘Virtual Machines’) or resource ID, and the portal instantly locates it. Advanced filters let you search by region, resource type, or tag.
Pro tip: Use the Recently Visited section to jump back to active projects without navigating menus.
Core Features of the Azure Portal Every User Should Know
The Azure Portal isn’t just a pretty interface — it’s packed with powerful features that streamline cloud operations. Let’s explore the essentials every user must master.
Azure Resource Manager (ARM) Integration
ARM is the backbone of resource deployment in Azure. Through the portal, you can deploy entire environments using ARM templates — JSON-based definitions that automate infrastructure setup.
For example, instead of manually creating a VM, network, and storage, you can deploy all three with a single click using a pre-configured template from the Azure Quickstart Templates gallery.
Monitoring with Azure Monitor and Metrics Explorer
Visibility is power. The Azure Portal integrates Azure Monitor, a comprehensive observability tool. From the portal, you can view CPU usage, network latency, and application logs in real time.
Use the Metrics Explorer to create custom charts, set up alerts, and correlate events across services. This is critical for proactive issue resolution.
Automation with Runbooks and Logic Apps
Repetitive tasks? Automate them. The portal lets you create runbooks in Azure Automation to restart VMs, clean up logs, or scale resources. Similarly, Logic Apps enable workflow automation across Azure and third-party services (e.g., send an email when a backup fails).
These tools reduce human error and free up time for strategic work.
Security and Identity Management in the Azure Portal
Security is not an afterthought — it’s built into the Azure Portal from the ground up. With cyber threats rising, understanding identity and access controls is essential.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) Explained
RBAC allows you to assign permissions based on roles. Instead of giving full admin rights, you can grant Reader, Contributor, or custom roles. For example, a developer might have ‘Contributor’ access to a dev resource group but only ‘Reader’ in production.
In the portal, go to Access Control (IAM) to assign roles. Always follow the principle of least privilege.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and Conditional Access
The Azure Portal supports MFA through Azure Active Directory (Azure AD). You can enforce MFA for all users or specific groups. Combine this with Conditional Access policies — like blocking logins from untrusted locations or requiring compliant devices.
These layers drastically reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
Azure Security Center and Compliance Dashboard
Microsoft Defender for Cloud (formerly Azure Security Center) provides a unified security management experience. In the portal, you’ll see a security score, recommendations, and threat alerts.
The Compliance Dashboard tracks adherence to standards like GDPR, HIPAA, and ISO 27001, making audits easier.
Cost Management and Billing Insights via Azure Portal
Cloud costs can spiral out of control without proper oversight. The Azure Portal offers robust tools to track, analyze, and optimize spending.
Understanding the Cost Analysis Tool
The Cost Analysis blade in the portal breaks down spending by service, resource group, or tag. You can view trends over time, compare months, and drill into specific charges.
For example, if your ‘Dev’ environment is consuming 40% of the budget, you can investigate and set limits.
Setting Budgets and Alerts
You can create budgets at the subscription or resource group level. When spending reaches 80% of the budget, the portal sends an email or triggers an Azure Function.
This proactive approach prevents billing surprises and encourages cost-conscious development.
Optimization Recommendations and Reserved Instances
The portal’s Cost Management module suggests optimizations — like resizing underutilized VMs or purchasing Reserved Instances for long-term savings (up to 72% off).
These recommendations are based on actual usage patterns, making them highly actionable.
Deployment and DevOps Integration with Azure Portal
The Azure Portal is not just for operations — it’s a key player in modern DevOps workflows. From CI/CD to infrastructure-as-code, the portal bridges development and deployment.
Using Azure DevOps Pipelines from the Portal
You can trigger Azure Pipelines directly from the portal. For example, when you deploy a web app, you can link it to a GitHub repository and automate builds and releases.
This integration ensures consistent, repeatable deployments across environments.
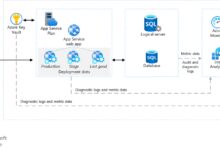
App Services and Web App Deployment Made Easy
Deploying a web application is as simple as clicking ‘Create’ in the App Services section. The portal guides you through configuration, offers staging slots, and enables auto-scaling.
You can also integrate with GitHub, Bitbucket, or Azure Repos for continuous deployment.
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) with ARM and Bicep
While the portal has a GUI, it fully supports IaC. You can export any resource group as an ARM template or use Bicep — a simpler, declarative language — to define infrastructure.
This ensures environments are version-controlled, auditable, and reproducible.
Advanced Tips and Hidden Gems in the Azure Portal
Even experienced users miss some of the portal’s most powerful features. Here are advanced tips to elevate your efficiency.
Keyboard Shortcuts and Accessibility Features
Did you know you can press Ctrl + / to open the command palette? Or use F1 to launch the help menu? These shortcuts speed up navigation.
The portal also supports screen readers and high-contrast modes, making it accessible to all users.
Using Cloud Shell Directly in the Browser
The Azure Cloud Shell is a free, browser-based terminal embedded in the portal. It comes with CLI, PowerShell, and common tools pre-installed.
No setup required — just click the >_ icon in the top bar and start scripting. Your home directory is backed by Azure Storage, so files persist across sessions.
Diagnostic Settings and Exporting Logs to Log Analytics
Enable diagnostic settings on any resource to stream logs to Azure Monitor Logs (Log Analytics). This allows advanced querying with Kusto (KQL) language.
For example, find all failed login attempts in the last 24 hours with a single query.
What is the Azure Portal?
The Azure Portal is a web-based interface provided by Microsoft for managing cloud services and resources on Microsoft Azure. It offers a graphical dashboard to deploy, monitor, and manage Azure resources like virtual machines, databases, and AI services.
How do I access the Azure Portal?
You can access the Azure Portal by visiting portal.azure.com and signing in with your Microsoft or Azure Active Directory account. Multi-factor authentication is recommended for security.
Is the Azure Portal free to use?
Yes, the Azure Portal itself is free to access. However, the resources you create and manage through it (like VMs or storage) incur costs based on usage. You can use the Cost Management tools to monitor and control spending.
Can I automate tasks in the Azure Portal?
Absolutely. The Azure Portal supports automation through Azure Automation runbooks, Logic Apps, and integration with Azure DevOps. You can also use the Cloud Shell to run CLI or PowerShell scripts for bulk operations.
What is the difference between Azure Portal and Azure CLI?
The Azure Portal is a graphical user interface (GUI), while Azure CLI is a command-line tool. The portal is ideal for visual management and learning, while CLI is better for scripting and automation. Both interact with the same Azure APIs.
Mastering the Azure Portal is essential for anyone working with Microsoft Azure. From intuitive navigation and robust security to cost control and DevOps integration, the portal offers a comprehensive suite of tools. Whether you’re deploying your first VM or managing enterprise-scale cloud environments, the Azure Portal is your command center. By leveraging its full capabilities — from ARM templates to real-time monitoring — you can streamline operations, enhance security, and optimize costs. The tips and features covered in this guide provide a solid foundation for both beginners and experts. As cloud technology evolves, staying proficient with the Azure Portal ensures you remain at the forefront of innovation and efficiency.
Further Reading: